Getting started with SVG
The Y axis is upside down
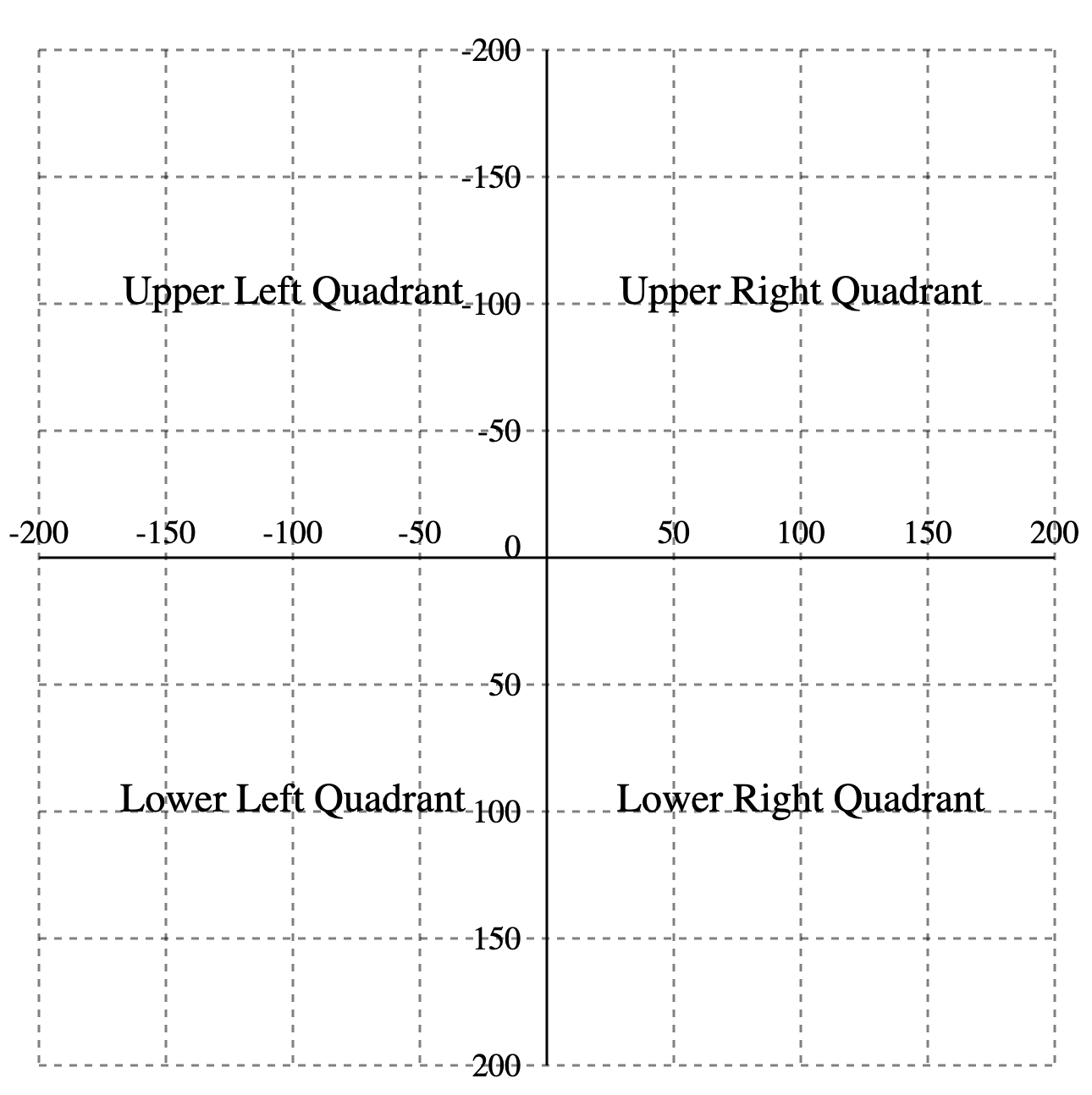
X and Y positions default to 0,0
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="300" height="300">
<circle r="100" fill="blue"/>
</svg>
Eek! Where’s the rest of the circle?
Use the viewBox attribute to move the image
- Spell
viewBoxcorrectly! - The
viewBoxattribute takes four whitespace-separated values:- minX (leftmost X position)
- minY (topmost Y position)
- width (always positive)
- height (always positive)
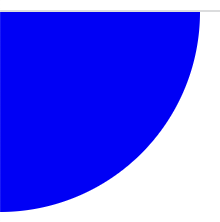
Draw where the arithmetic is easy and move with viewBox:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="300" height="300"
viewBox="-50 -50 100 100">
<circle r="100" fill="blue"/>
</svg>
Bar chart with heights of 50, 35, and 15
Drawing it in positive space (lower right quadrant) makes for odd arithmetic:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="300" height="300">
<rect x="0" y="50" height="50" width="20" fill="blue"/>
<rect x="30" y="65" height="35" width="20" fill="red"/>
<rect x="60" y="85" height="15" width="20" fill="green"/>
</svg>
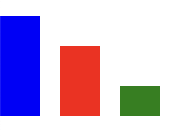
Eek! Where did 65 and 85 come from?
For easier arithemtic, draw in the upper right quadrant
Use negative Y values with matching positive heights, so that all bars grow down to the y=0 position …
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="300" height="300">
<rect x="0" y="-50" height="50" width="20" fill="blue"/>
<rect x="30" y="-35" height="35" width="20" fill="red"/>
<rect x="60" y="-15" height="15" width="20" fill="green"/>
</svg>
Now the 35 bar has only 35 (no 65) and 15 has only 15 (not 85), but …
… this won’t be visible until we move it down with viewBox:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="300" height="300"
viewBox="0 -100 100 100">
<rect x="0" y="-50" height="50" width="20" fill="blue"/>
<rect x="30" y="-35" height="35" width="20" fill="red"/>
<rect x="60" y="-15" height="15" width="20" fill="green"/>
</svg>
viewBox can scale an image
- See http://dh.obdurodon.org/coordinate-tutorial.xhtml for brief information about how to scale with
viewBox. - See Sara Soueidan’s Understanding SVG coordinate systems and rransformations (Part 1) — The viewport, viewBox, and preserveAspectRatio for detailed information about
viewBoxand more.